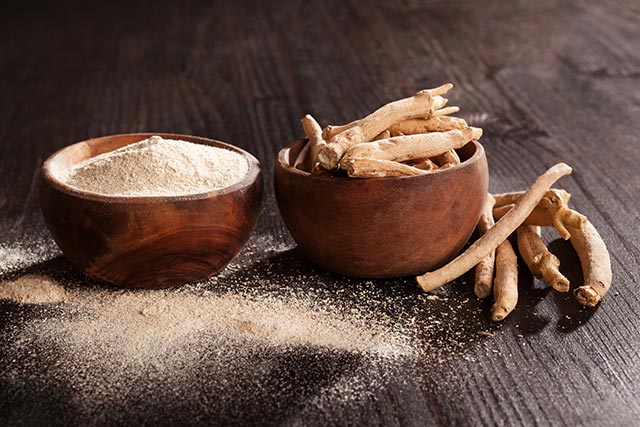
Root extract of Ashwagandha shows promising results in modulating cancer cachexia
10/18/2018 / By Edsel Cook

Cachexia is the weakness and wasting of the body that stems from cancer, inflammation, and other chronic ailments. An Indian research team believe that an extract from the root of the ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) can help amend cachexia in cancer patients.
The study was supported by Manipal University. The results came out in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Ashwagandha roots were processed to produce a water-based (aqueous) extract. The solution was applied to leukemic THP-1 cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
- The extract was run through numerous tests to determine its toxicity against leukemic cells and PBMCs and its antioxidant activity. The concentrations of glutathione, caspase activity, and adenosine triphosphate levels were also measured. Finally, the tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, -1 beta, and -10 levels were analyzed.
- During the first day, the extract decreased the viability of PBMC while also increasing that of THP-1 cells. By the third day, this trend reversed, with PBMC becoming more viable while the leukemic cells grew less viable.
- The ashwagandha extract increased the amount of oxidants scavenged in both the PBMC culture and the THP-1 leukemic cell culture. It also reduced the concentrations of inflammatory cytokines. Finally, it increased the death of cells, especially cancer cells.
- For THP-1 cancer cells, the extract reduced the levels of cytokines that encouraged the production of inflammation-causing substances.
Based on their findings, the researchers believed that ashwagandha root extract could be used to improve cancer-related cachexia and reduce the runaway growth of leukemic cells.
Check out the full report at this link.
For more articles about ashwagandha and other natural anti-cancer approaches, visit AntiCancer.news.
Journal Reference:
Naidoo DB, Chuturgoon AA, Phulukdaree A, Guruprasad KP, Satyamoorthy K, Sewram V. WITHANIA SOMNIFERA MODULATES CANCER CACHEXIA ASSOCIATED INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES AND CELL DEATH IN LEUKAEMIC THP-1 CELLS AND PERIPHERAL BLOOD MONONUCLEAR CELLS (PBMC’S). BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 10 April 2018;18(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2192-y
Tagged Under: anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidants, ashwagandha, cachexia, herbal medicine, Herbs, Indian ginseng, inflammation, natural cures, natural medicine, remedies