Healthy and nutritious: 9 Reasons to eat more oat bran
10/03/2019 / By Melissa Smith
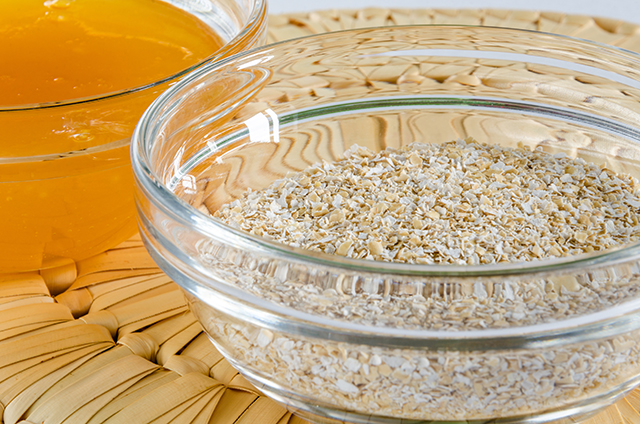

Oat bran is a piece of an oat grain (Avena sativa), which is harvested and processed to remove the inedible outer part of the grain. This leaves behind the oat groat, which sits below the inedible hull. Oat bran is the outer layer of the oat groat.
Oat bran and oatmeal come from the oat grain, but oat bran is healthier. It is less processed and contains more vitamins, minerals, and fiber than oatmeal. It is also linked to many health benefits. (Related: Oats and gut health: The best breakfast has vitamins and fiber to keep your gut moving.)
Here are nine reasons why you should consider eating more oat bran:
- It is nutritious – Oat bran has similar amounts of carbs and fat as regular oatmeal, but it contains more protein and fewer calories. It is also high in fiber, especially beta-glucan. Oat bran also offers good amounts of thiamine, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, riboflavin, and potassium. You can also get small amounts of folate, vitamin B6, niacin, and calcium.
- It is rich in antioxidants – Oat bran offers high amounts of polyphenols, which are plant-based molecules that act as antioxidants. Antioxidants protect the body from free radicals that damage cells and cause diseases. Oat bran is especially rich in phytic acid, ferulic acid, and avenanthramides – which have been associated with reduced inflammation, anti-cancer properties, and lower blood pressure.
- It keeps your heart healthy – Eating oat bran may help you avoid heart disease risk factors, such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure. The beta-glucan in oat bran can reduce cholesterol levels by helping to remove cholesterol-rich bile – a substance that aids in fat digestion. Its beta-glucan content also lowers blood pressure. The avenanthramides in oat bran also work together with vitamin C to prevent the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
- It regulates blood sugar – Like other foods rich in soluble fiber, oat bran may help control blood sugar. Soluble fiber like beta-glucan helps slow the digestion and absorption of carbs, which stabilizes blood sugar levels.
- It aids in digestion – Because of its high fiber content, oat bran can help improve digestion. Oat bran provides both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber helps soften stool, while insoluble fiber can make stool bulkier and easier to pass. Eating oat bran may help relieve constipation and other digestive problems.
- It may relieve inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) – Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are two types of IBS both characterized by chronic bowel inflammation. Eating oat bran may provide IBD relief because of its high fiber content, which good gut bacteria break down into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate. These fatty acids nourish colon cells and reduce bowel inflammation.
- It may ward off colorectal cancer – Adding oat bran to your diet may also lower your risk of colorectal cancer. Its soluble fibers serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, which ferment fiber and produce SCFAs. The antioxidants in oat bran may also inhibit cancer growth.
- It helps with weight loss – If you’re trying to shed those extra pounds, consider adding oat bran to your weight loss diet. This fiber-rich food helps suppress your appetite by reducing hunger hormones like ghrelin.
- It is easy to add to your diet – Oat bran is delicious, versatile, and easy to add to your regular diet. You can eat it as a hot cereal or mix it into bread dough and muffin batter. You can also add it raw to cereals, yogurts, and smoothies.
Things to consider when buying oat bran
Before buying oat bran products like oat bran bread, cereals, and crackers, or any packaged food, it is important to read the label first. Make sure that there aren’t excess amounts of sugar or sodium, which may negate the potential health benefits you could get from oat bran.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, antioxidants, Avena sativa, beta-glucan, blood sugar, cholesterol, clean food, diabetes, dietary fiber, digestion, digestive health, disease treatments, fiber, fightobesity, functional food, gut health, heart health, immune system, inflammatory bowel disease, natural cures, natural medicine, nutrients, Oat bran, oatmeal, oats, prevention, remedies, slender, soluble fiber, weight loss, whole grains
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
Antioxidants.News is a fact-based public education website published by Antioxidants News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Antioxidants News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.