Curcumin is a powerful polyphenol that can combat the effects of chronic stress
11/28/2018 / By Ellaine Castillo
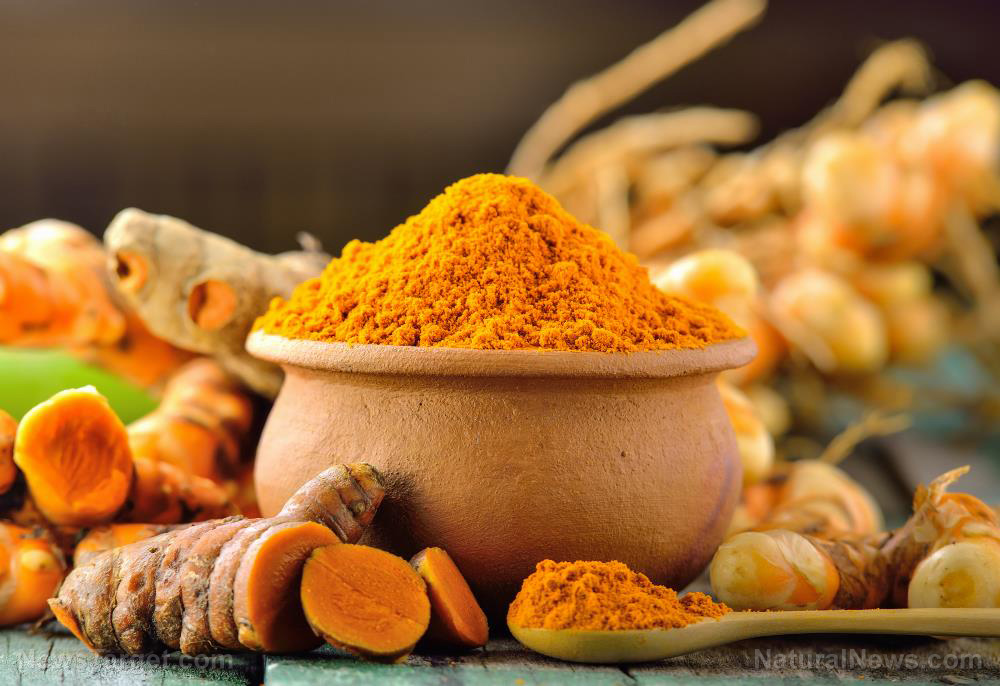

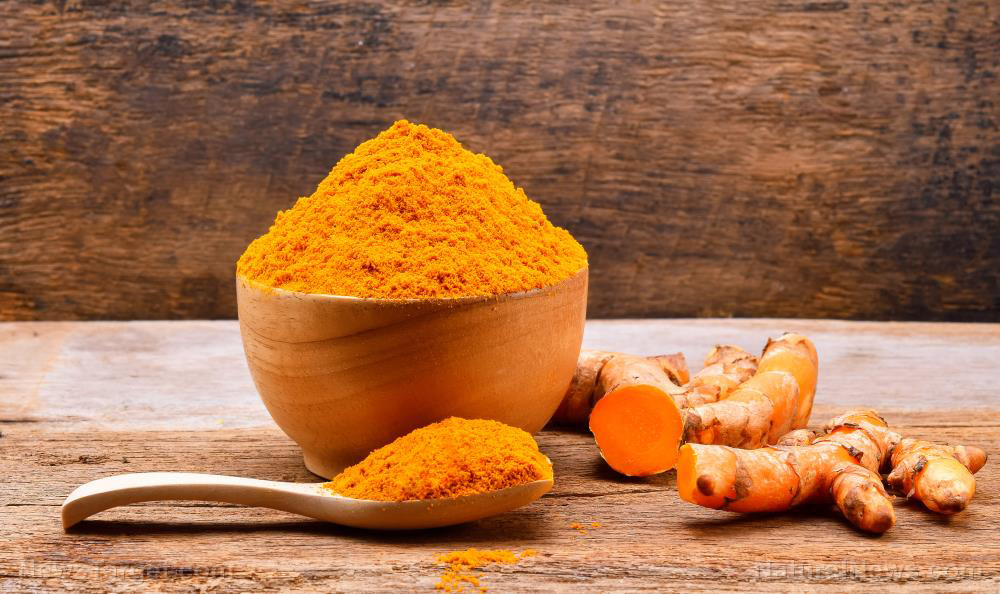
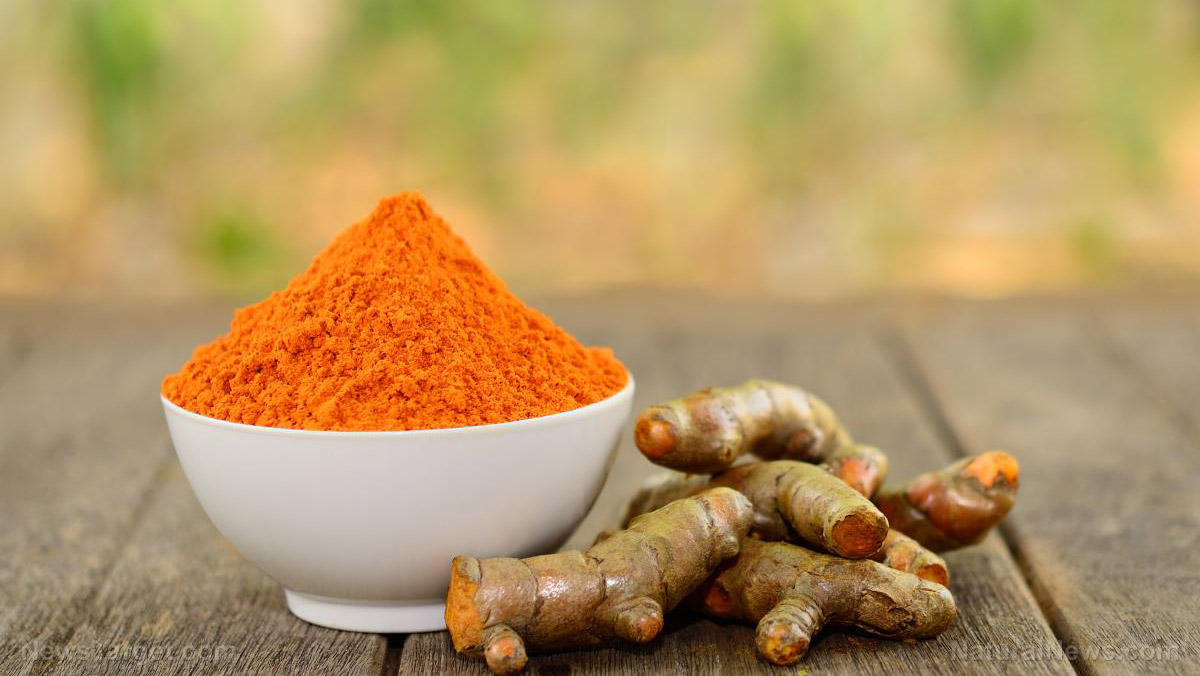
Turmeric has been used to add flavor and color to food for thousands of years, but over the last decade, it has gained worldwide popularity not for its use in the kitchen but because of its many health benefits. Although there is already a long list of beneficial properties that this golden herb has, researchers continue to find even more reasons why people should include this in their diet. Recent studies found that curcumin, the main active ingredient in turmeric, can prevent the harmful effects of chronic stress.
With everything that’s going on in the world, it’s normal to feel stressed. However, constantly being in this state can have repercussions on a person’s health. This condition, known as chronic stress, is characterized by increased production of the stress hormone cortisol and a consequent increase in the size and weight of the adrenal glands that produce it. Moreover, it also prevents antioxidants from neutralizing harmful free radicals, thereby allowing them to induce oxidative damage on the cells. Collectively, these effects increase a person’s risk for health problems especially those that are related to brain functions, such as anxiety, depression, poor memory and concentration, and sleep problems. Fortunately, there are natural remedies like turmeric that can reverse these changes.
Among the 100 compounds found in turmeric, the yellow pigment curcumin remains the most popular even if it makes up just about five percent of the spice. This is because of the wide array of benefits associated with this compound. Its ability to reverse the effects of chronic stress is one of its most recently proven benefits. This was observed through multiple studies – not just in animal models but even in human clinical trials.
How does curcumin reverse the effects of chronic stress?
Curcumin works against chronic stress in various ways. One of these is by improving hormone balance, which it does by restoring normal adrenal gland functions to reduce cortisol production. Moreover, it also increases the levels of the mood-boosting brain chemicals serotonin and dopamine by stimulating their production and inhibiting the activity of enzymes that break them down. These results are especially advantageous for patients who suffer from chronic stress-induced depression since most prescription antidepressants that work in the same manner as curcumin have side effects like nausea, fatigue, seizures, stroke, and heart attacks.
Another way through which curcumin improves chronic stress is by reducing biological indicators of this condition, which include amylase in saliva. It also lessens the number of free radicals present using its antioxidant properties. Furthermore, curcumin prevents brain cells from dying and even facilitates the production of new connections between them.
With all these biological properties, curcumin effectively reduces the risk of diseases like depression, anxiety, Alzheimer’s, dementia, and Parkinson’s. Moreover, it also improves brain functions such as memory, concentration, alertness, and cognition. (Related: Curcumin found to prevent brain degenerative diseases including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.)
Other health benefits of curcumin
Curcumin can be acquired just by eating turmeric, but researchers have also come up with supplements that provide exact doses of this compound. By increasing your intake of curcumin, you can enjoy many health benefits, which include the following:
- Improved digestive health
- Elimination of microbes
- Protection against heavy metals and fluoride
- Promotion of weight loss
- Regulation of blood sugar and cholesterol levels
- Delayed aging
- Reduced severity of premenstrual syndrome
- Prevention of cataracts and dry eyes
- Lowered risk of cancer
For more articles about the health benefits of curcumin, visit Turmeric.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Brain, chronic stress, curcumin, health benefits, mental health problems, natural remedies, neurodegenerative diseases, polyphenols, prevention, stress, turmeric